watch 方法
vue 的 watch 方法用来监听 vue 中 data 的变动, 可以接受一个函数, 对象, 字符串, 或者数组。watch 方法接受两个参数: deep & immediate, immediate 表明是否立即进行函数调用, deep 表示是否监听更深一级的对象;例如在vue 组件中:1 | new Vue({ |
this.data 发生重新赋值的时候, 就会调用 watch 中 data 后面跟的匿名函数:在 vue.js 中, 调用流程如下:首先, 因为在 vue watch 中的名称是先写在 data 中的,在初始化 watch 方法之前, 首先对于 data 中的数据进行了初始化,调用了 defineReactive 方法, 将其数据设为响应式的数据初始化
watch方法:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18// 初始化状态
// vm: vue 实例
function initState (vm) {
vm._watchers = [];
var opts = vm.$options;
if (opts.props) { initProps(vm, opts.props); }
if (opts.methods) { initMethods(vm, opts.methods); }
if (opts.data) {
initData(vm);
} else {
observe(vm._data = {}, true /* asRootData */);
}
if (opts.computed) { initComputed(vm, opts.computed); }
if (opts.watch && opts.watch !== nativeWatch) {
// 初始化 watch
initWatch(vm, opts.watch);
}
}initWatch为如下方法:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14// 对于 vue watch 方法中的每一个键都创建一个 watcher
function initWatch (vm, watch) {
for (var key in watch) {
var handler = watch[key];
// 当watch 键后面跟着一个数组的时候, 对于数组里面的每一个函数, 都调用 createWatcher 方法
if (Array.isArray(handler)) {
for (var i = 0; i < handler.length; i++) {
createWatcher(vm, key, handler[i]);
}
} else {
createWatcher(vm, key, handler);
}
}
}createWatcher方法: 用于在watch中某个键的相关字段进行解析:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22// vm: vue 实例
// expOrFn: 创建 watcher 的一些数据名称
// hander 回调函数
function createWatcher (
vm,
expOrFn,
handler,
options
) {
// 当执行函数是一个对象的时候, 这个时候是将 handler 的 handler调用给执行函数
// 这里的 options 是 watch 函数的配置信息
if (isPlainObject(handler)) {
options = handler;
handler = handler.handler;
}
// 当 handler 是一个字符串的时候, 会调用 vm 中相应的方法
if (typeof handler === 'string') {
handler = vm[handler];
}
//调用在 vue 实例 vm 上面的 $watch 方法
return vm.$watch(expOrFn, handler, options)
}调用 vue 实例上面的
$watch方法, 这个方法会对于当前的方法创建一个观察者watcher1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28Vue.prototype.$watch = function (
expOrFn,
cb,
options
) {
var vm = this;
if (isPlainObject(cb)) {
return createWatcher(vm, expOrFn, cb, options)
}
options = options || {};
options.user = true;
// 创建一个新的观察者
var watcher = new Watcher(vm, expOrFn, cb, options);
// 当可选项中包含有 immediate 属性的时候
if (options.immediate) {
try {
// 立即执行当前 watch 函数
cb.call(vm, watcher.value);
} catch (error) {
handleError(error, vm, ("callback for immediate watcher \"" + (watcher.expression) + "\""));
}
}
// 返回一个取消 watch 的函数
return function unwatchFn () {
watcher.teardown();
}
};
}当 调用 watch 方法的时候, 将当前
watch内data的回调函数作为依赖进行收集。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83var Watcher = function Watcher (
vm,
expOrFn,
cb,
options,
isRenderWatcher
) {
this.vm = vm;
if (isRenderWatcher) {
vm._watcher = this;
}
vm._watchers.push(this);
// options
if (options) {
this.deep = !!options.deep;
this.user = !!options.user;
this.lazy = !!options.lazy;
this.sync = !!options.sync;
this.before = options.before;
} else {
this.deep = this.user = this.lazy = this.sync = false;
}
// 回调函数被绑定到 Watcher 观察者上面的 cb 属性上面
this.cb = cb;
this.id = ++uid$1; // uid for batching
this.active = true;
this.dirty = this.lazy; // for lazy watchers
this.deps = [];
this.newDeps = [];
this.depIds = new _Set();
this.newDepIds = new _Set();
this.expression = expOrFn.toString();
// parse expression for getter
if (typeof expOrFn === 'function') {
this.getter = expOrFn;
} else {
// 这里对于监听的变量值进行解析
this.getter = parsePath(expOrFn);
console.log('this.getter', this.getter);
if (!this.getter) {
this.getter = noop;
warn(
"Failed watching path: \"" + expOrFn + "\" " +
'Watcher only accepts simple dot-delimited paths. ' +
'For full control, use a function instead.',
vm
);
}
}
this.value = this.lazy
? undefined
: this.get();
};
/**
* Evaluate the getter, and re-collect dependencies.
*/
Watcher.prototype.get = function get () {
// 将当前的 Watcher 赋值给 Dep.target
pushTarget(this);
var value;
var vm = this.vm;
try {
// 调用 getter 方法, 触发响应式数据的 get 属性, 进行依赖搜集
value = this.getter.call(vm, vm);
console.log('this.value', value);
} catch (e) {
if (this.user) {
handleError(e, vm, ("getter for watcher \"" + (this.expression) + "\""));
} else {
throw e
}
} finally {
// "touch" every property so they are all tracked as
// dependencies for deep watching
if (this.deep) {
traverse(value);
}
popTarget();
this.cleanupDeps();
}
return value
};parsePath方法用于监听的字段进行解析:当触发响应式数据的1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17var bailRE = new RegExp(("[^" + (unicodeRegExp.source) + ".$_\\d]"));
function parsePath (path) {
if (bailRE.test(path)) {
return
}
// 按照 . 号进行分割为数组, 适用于我们想要监听一个对象下面的某一个属性的时候
var segments = path.split('.');
// 返回的函数作为 上面代码中的 this.getter
// 当调用 this.getter 函数的时候, 会触发在当前数据上面的响应式数据的 get 方法, 搜集依赖
return function (obj) {
for (var i = 0; i < segments.length; i++) {
if (!obj) { return }
obj = obj[segments[i]];
}
return obj
}
}getter属性的时候,在defineReactive中, 会进行依赖收集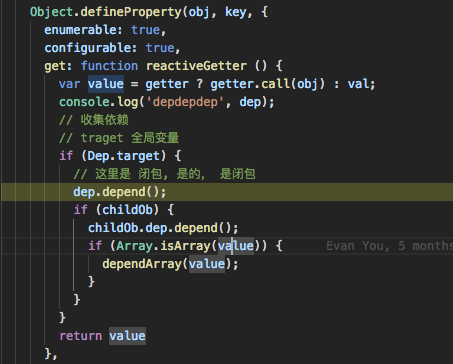 当调用
当调用dep.depend()的时候, 调用了Dep类的depend方法:这里的1
2
3
4
5Dep.prototype.depend = function depend () {
if (Dep.target) {
Dep.target.addDep(this);
}
};Dep.target是我们之前将watcher赋值的那一个, 当调用Watcher上面的addDep方法的时候, 是将当前的dep传入watcher实例中的newDeps属性, 并且, 当前dep实例上面的addSub方法将会将Watcher存放到 这个实例的subs属性上面。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10Watcher.prototype.addDep = function addDep (dep) {
var id = dep.id;
if (!this.newDepIds.has(id)) {
this.newDepIds.add(id);
this.newDeps.push(dep);
if (!this.depIds.has(id)) {
dep.addSub(this);
}
}
};当依赖收集完毕之后, 当监听的值发生变化的时候,通知依赖发生变化:
当监听的数据发生变化的时候, 会调用这个数据的set属性:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23set: function reactiveSetter (newVal) {
// 获取到原来的值
var value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val;
/* eslint-disable no-self-compare */
// 当要监听的数据没有发生变化的时候, 返回
if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) {
return
}
/* eslint-enable no-self-compare */
if (customSetter) {
customSetter();
}
// #7981: for accessor properties without setter
if (getter && !setter) { return }
if (setter) {
setter.call(obj, newVal);
} else {
val = newVal;
}
childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal);
// 通知依赖发生变化
dep.notify();
}dep.notify()是用来通知依赖发生变化的, 调用了dep实例上面的notify方法:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14Dep.prototype.notify = function notify () {
// stabilize the subscriber list first
var subs = this.subs.slice();
if (!config.async) {
// subs aren't sorted in scheduler if not running async
// we need to sort them now to make sure they fire in correct
// order
subs.sort(function (a, b) { return a.id - b.id; });
}
// subs 中存放的是 watcher , 调用了 watcher 实例的 update 方法。
for (var i = 0, l = subs.length; i < l; i++) {
subs[i].update();
}
};在1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11Watcher.prototype.update = function update () {
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (this.lazy) {
this.dirty = true;
} else if (this.sync) {
this.run();
} else {
// 调用 queueWatcher
queueWatcher(this);
}
};queueWatcher方法中, 将当前变动的所有watcher存放数组queue中:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33/**
* Push a watcher into the watcher queue.
* Jobs with duplicate IDs will be skipped unless it's
* pushed when the queue is being flushed.
*/
function queueWatcher (watcher) {
var id = watcher.id;
if (has[id] == null) {
has[id] = true;
if (!flushing) {
// 将 watcher 存入
queue.push(watcher);
} else {
// if already flushing, splice the watcher based on its id
// if already past its id, it will be run next immediately.
var i = queue.length - 1;
while (i > index && queue[i].id > watcher.id) {
i--;
}
queue.splice(i + 1, 0, watcher);
}
// queue the flush
if (!waiting) {
waiting = true;
if (!config.async) {
flushSchedulerQueue();
return
}
nextTick(flushSchedulerQueue);
}
}
}执行
watch中数据变动之后的函数回调:调用。flushSchedulerQueue调用1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42function flushSchedulerQueue () {
currentFlushTimestamp = getNow();
flushing = true;
var watcher, id;
// Sort queue before flush.
// This ensures that:
// 1. Components are updated from parent to child. (because parent is always
// created before the child)
// 2. A component's user watchers are run before its render watcher (because
// user watchers are created before the render watcher)
// 3. If a component is destroyed during a parent component's watcher run,
// its watchers can be skipped.
queue.sort(function (a, b) { return a.id - b.id; });
// do not cache length because more watchers might be pushed
// as we run existing watchers
for (index = 0; index < queue.length; index++) {
watcher = queue[index];
if (watcher.before) {
watcher.before();
}
id = watcher.id;
has[id] = null;
// 调用 watcher 实例上面的 run 方法
watcher.run();
// in dev build, check and stop circular updates.
if (has[id] != null) {
circular[id] = (circular[id] || 0) + 1;
if (circular[id] > MAX_UPDATE_COUNT) {
warn(
'You may have an infinite update loop ' + (
watcher.user
? ("in watcher with expression \"" + (watcher.expression) + "\"")
: "in a component render function."
),
watcher.vm
);
break
}
}
}watcher.run方法之后, 如下:最终, 调用1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27Watcher.prototype.run = function run () {
if (this.active) {
var value = this.get();
if (
value !== this.value ||
// Deep watchers and watchers on Object/Arrays should fire even
// when the value is the same, because the value may
// have mutated.
isObject(value) ||
this.deep
) {
// set new value
var oldValue = this.value;
this.value = value;
if (this.user) {
try {
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue);
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, this.vm, ("callback for watcher \"" + (this.expression) + "\""));
}
} else {
// 调用 watch 之后的函数方法, 传入的两个值, 当前变动的值和之前的值
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue);
}
}
}
};this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue);执行当监听的数据发生变化时候的回调函数, 调用的时候传入两个参数: value && oldValue, 表示当前的值和变化之前的值。
deep 为 true 的时候, 这个时候, 当对象中的某个属性发生变化的时候, 也会被监听到变动, 关于 deep 为 true 的代码在下面:1 | Watcher.prototype.get = function get () { |
deep 为 true 的时候, 调用 traverse 方法, 这个方法的作用是出发对象中每一个属性的 get 方法, 从而让他们的依赖得以收集:traverse. 方法:1 | // 递归调用对象中的属性, 通过 val[i] 或者 val[key[i]] 触发 get 方法 |